Shagbark hickory, Carya ovata Bitternut hickory, Carya cordiformis T he volume in hickory has increased steadily over the last several decades and is aging Since 19, the volume in large trees has more than tripled while the volume in small trees has only increased 21% GThe bitternut hickory is abundant and can be found across much of the eastern and midwestern United States Found in rich, moist woods, the bitternut can tolerate shade in its youth, but needs full sun at maturity Attributes The bitternut hickory is a medium tree with a long, clear trunk and leaves composed of 79 elliptical leafletsZ = Tree's Average Crown Spread (Feet);

Bitternut Hickory Natural Resource Stewardship
Bitternut hickory leaf id
Bitternut hickory leaf id-University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture Cooperative Extension Service Horitculture Landscape Tree Identification Bitternut Hickory Javascript must be enabled for the correct page display skip to main contentBitternut Hickory Carya cordiformis (Wangenh) K Koch Bitternut Hickory Photo Library Click on an image below for a gallery of that part of the tree Please contact me before reusing any images Thanks General description Etymology




A Beginner S Guide How To Identify Hickory Nuts Mossy Oak
Hickory Tree Identification The best way to identify hickory trees is by their bark, leaves, and nuts Hickory leaves are long with up to 17 pointed leaflets growing oppositely on each leaf stem Hickory tree bark is ridged and gray and peels easily when the tree matures Nuts from the common hickory trees are sweetFamily Juglandaceae Latin Name Carya cordiformis Common Name (s) Bitternut, bitternut hickory, swamp hickory Deciduous or Evergreen Deciduous Native Range Eastern United States USDA Hardiness Zone 49 Mature Height 5080' Mature Spread 3050' Bloom Time AprilMayBitternut hickory comprised approximately 35% of the trees in the stands Eighteen poletimbersized bitternut hickory trees (13–28 cm in diameter at 14 m) with healthy crowns (
Carya cordiformis – Bitternut Hickory At its northern range in the Ottawa Valley and west Quebec, Bitternut Hickory is a large, stately tree distributed across the Ottawa area in woodlands and urban natural areas It is the only native, naturally occurring hickory that grows this far north (One exception is a singular population of ShagbarkBitternut hickory is a mediumsized tree with a long, clear trunk and broad, spreading crown Leaves are alternate, pinnately compound, 6–12 inches long, with 7–9 elliptical, toothed leaflets Leaflets dark yellowgreen and smooth above, pale and slightly hairy below, on hairy stalks Bitternut Hickory Wood Color/Appearance Heartwood tends to be light to medium brown, with a reddish hue and sapwood is a paler yellowishbrown Bitternut Hickory Tree Identification Tree A Tree is about ft (3040 m) in height and the trunk diameter can be 250 to 350 ft It is a fruitbearing tree with a relatively narrow crown Nut/fruit
Bitternut Hickory (Carya cordiformis) has sulfuryellow buds that appear to lack bud scalesIt is the only Michigan tree species with yellow budsShagbark Hickory (Carya ovata) has a large terminal bud with spreading outer bud scalesThe lateral buds are smallerTrees Page Menu Bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) Click on the images help you identify an Bitternut hickory Form Height 40' to 75', diameter 10" to 25";Scientific Name Carya cordiformis Family Juglandaceae (walnuts) Description Bitternut hickory is a mediumsized tree with a long, clear trunk and broad, spreading crown Leaves are alternate, pinnately compound, 6–12 inches long, with 7–9 elliptical, toothed leaflets




Hickory Trees Types Bark Leaves Nuts Pictures Identification




Carya Cordiformis Bitter Hickory Bitternut Bitternut Hickory Bitter Pecan Pig Hickory Red Hickory Swamp Hickory White Hickory North Carolina Extension Gardener Plant Toolbox
Shellbark hickory is the smallest of the hickory species with a trunk thickness of one to three feet and grows 3060 feet tall The pignut hickory trees can grow about 50 to 70 feet in height and have the same thickness as mockernut and bitternut hickory treesHickories are trees in the genus Carya There are 9 species that grow naturally in Missouri All have alternate, feathercompound leaves with 5–13 unlobed leaflets per leaf The largest leaflets are often near the leaf tip, though in some species they are uniform or have the middle leaflets larger In nearly all our species, the leaflet margins are toothed Hickory leaves typically turnBitternut hickory Carya cordiformis Bitternut hickory is one of four hickory species (along with mockernut, pignut, and shagbark) that are common in Delaware In general, hickory trees are identifiable by their alternate, compound leaves Much like other hickories, bitternut displays brilliant yellow fall color



Winter Trees Bitternut Hickory Outside My Window




Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory Trees Canadensis
The leaflets that become smaller towards the base of the compound leaf resemble those of the related Juglans (Black Walnut, Butternut) species as well as those of the unrelated Fraxinus (Ash) species, but Juglans have sticky hairs and more numerous leaflets, and Fraxinus have rather different flowers and fruits, and its leaflets are often shortstalked But Bitternut Hickory mayThe bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) is a tall slender tree, 60 to 80 feet tall It is found on moist sites on upper flood plains and at the bottom of slopes It is widely distributed over the eastern United States as far west as Kansas and Nebraska In Iowa it is found quite widely throughout the state except in the northwestern partIdentification Description Foliage 57 leaflets, serrate, narrowly ovate to lanceolate, base leaflets smaller than terminal leaflet Leaf Type Compound Pinnate Needles 0 Bark light gray/brown, smooth when young, then lightly textured shallow and narrow fissures with age




10 Different Types Of Hickory Wood Plus Important Facts Home Stratosphere




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis
GENERAL BOTANICAL CHARACTERISTICS Bitternut hickory is a mediumtolarge native, deciduous tree, typically reaching a height of 60 to 80 feet (14 m) 11,13Under a forest canopy, it develops a long branchfree trunk with little taper, and a short rounded crown of slender ascending branches that broaden the crown toward the topBitternut Hickory (Carya cordiformis),found throughout all of Ohio, is a common Hickory that has bitter nuts usually too illfit for human consumption, as its name impliesIt is unlike Shagbark and Shellbark Hickories in more ways than this, in that its leaflets are more lanceshaped, its fruits have fourwinged husks and are thinshelled, its bark is sinewy when young with crisscrossingTall and slender with straight, green trunk and broad, rounded crown Bark Granitegray, faintly tinged with yellow;



Virginia Tech Dendrology Fact Sheet



Texas A M Forest Service Trees Of Texas List Of Trees
Bitternut hickory is named for its acrid nuts, which are eaten by very few animal species Its deciduous compound leaves are toothed The wood is hard and heavy, but useful for making many types of furniture, paneling, and tools The dense wood also yields a useful charcoalBitternut hickory Juglandaceae Carya cordiformis (Wangenh) K Koch symbol CACO15 Leaf Alternate, pinnately compound, 7 to 10 inches long, with 7 to 11 leaflets, leaflets are lanceolate and serrate, rachis is slender and pubescent, dark green above, paler below Flower Species is monoecious;Identification of Butternuts and Butternut Hybrids Lenny Farlee1,3, Keith Woeste1, Michael Ostry2, James McKenna1 and Sally Weeks3 1 USDA Forest Service Hardwood Tree Improvement and Regeneration Center, Purdue University, 715 W State Street, West Lafayette, IN, 2 USDA Forest Service Northern Research Station, 1561 Lindig Ave St Paul, MN




Hickory Nuts Foraging For Pignut And Shagbark Hickory Nuts Hickory Tree Hickory Tree Id




Updated Summer Tree Id Practice Cyber
Bitternut Hickory – VA Trees of the same species are compared using the following calculation x = Tree Trunk Circumference (Inches);These leaves are also aromatic Even bitternut hickory leaves have a slightly downy underside Even though, the leaf color is green in different hickory species, you may find them in different shades Shagbark hickory tree has yellowishgreen leaves, whereas, nutmeg hickory leaves have a whitish underside with dark green upper surfacePurdue Extension forester Lenny Farlee shares more about this species, which features relatively narrow leaflets, strong sulphur yellow colored elongated buds and a tight light gray colored bark with small interlacing ridges If you have any questions regarding trees, forests, wildlife, wood products




Evergreen Bitternut Hickory Tree Flat Design Stock Vector Royalty Free



Winter Trees Bitternut Hickory Outside My Window
Y = Tree Height (Feet);Bitternut Hickory is a tall, slender, cylindrical deciduous tree with a broad pyramidshaped crown It is native to North Carolina and usually found on moist rich soils in relatively open areas where the tree can find sun The Bitternut Hickory does not tolerate shade but will tolerate a Bitternut hickories have 711 leaflets per twig, and their foliage is a dark green above and a paler green below The shape of the leaves is thin and lanceolate "Yellowbud" hickory The nuts of bitternut hickory come singly or in clusters of 2 or more These trees bear annually, every season, and with a consistent crop




How To Identify Hickory Trees 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Bitternut Hickory Ohio Department Of Natural Resources
Carya cordiformis, commonly called bitternut hickory, is a medium to large, broadly columnar, deciduous tree that typically grows 5080' tall with an irregular, ovalrounded crown It is native to forested areas (wet bottom lands to some upland dry sites) in Identify a Bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) This species grows in moist forest, also called steam banks The leaflets, which grow 9 to a rachis, are broad and smooth around the edges The bitternut hickory fruit grows to be between 08 inch (2 cm) and 16 inches (4 cm) long, and is enclosed in a thin, dark brown huskBroken into thin, platelike scales Leaf
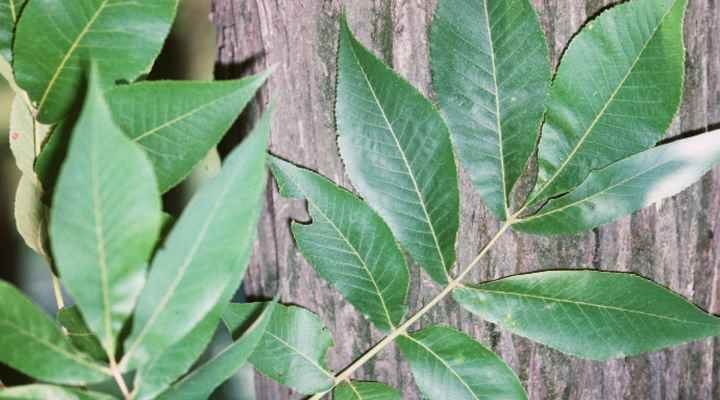




Hickory Trees Types Bark And Leaves Identification Guide With Pictures Eathappyproject
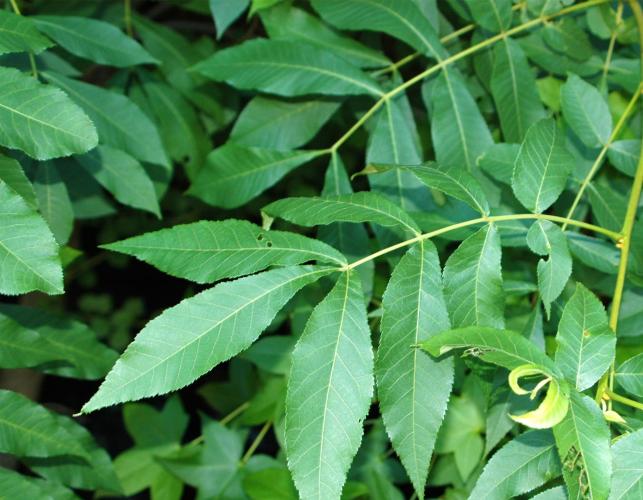




Bitternut Hickory Missouri Department Of Conservation
The bitternut hickory is a very well populated tree and covers many provinces and states on the eastern side of North America They prefer more temperate climates and can be found in the USDA hardiness zones 4 through 9 In the United States, they grow naturally in the following areas southwestern New Hampshire Bitternut Hickory Native Range Carya cordiformis, or Bitternut Hickory, is native to Kansas and Eastern United States Mature Size It is a large tree with an oval crown reaching a height of 50 to 80 feet Growth Rate It has a slow growth rate Leaves, Stems and Fruit The compound leaves, 612 inches long, with 59 leafletsCommon Name bitternut, bitternut hickoryScientific NameFamily JuglandaceaeGenus CaryaSpecies cordiformisHardiness Zone 4 to 9Height 50 to 80 ftWidth 30 to 50 ftCommon Characteristics Bitternut hickory is a tall tree with a broad and round crown Its name comes from the bitter, inedible nuts that the tree produces
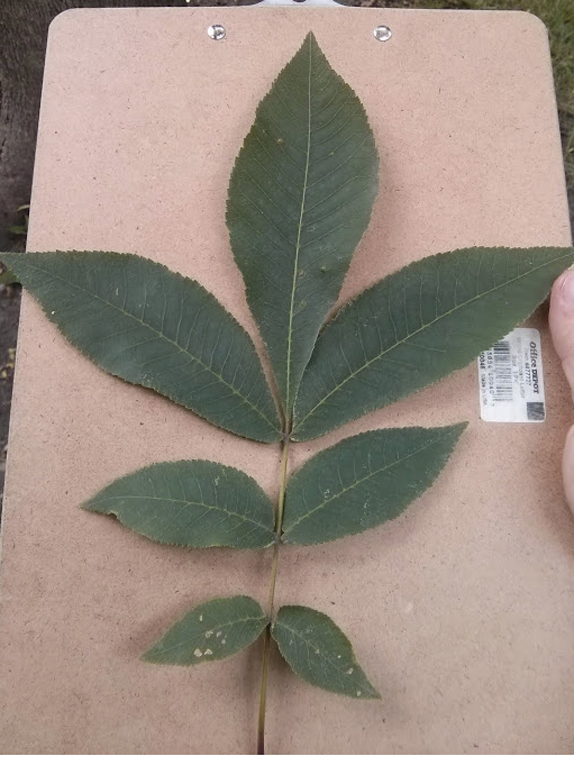




Basic Tree Tree Identification Regional And Community Forestry School Of Natural Resources Unviersity Of Nebraska Lincoln




Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory Double E Gardens
Bitternut hickory Bitternut hickory, or Carya cordiformis, grows in dense, wet forests and produces smaller fruit, growing from less than an inch to 16 inches long The husk is thin and dark, and the fruit is quite bitter While not poisonous, they are best left for the squirrels and other wildlife, given their unpleasant taste Pignut hickory Bitternut Hickory Tree Nut Identification The identifying features of the bitternut hickory tree are its large leaves with seven to eleven leaflets, rounded hard nuts, and gray bark that develops ridges as it matures Red Hickory Nut (Carya ovalis)Bitternut hickory is s a medium sized tree becoming rounded with age It's distinguished by its smooth bark and sulfuryellow buds The pinnate leaves typically have 59 brightgreen leaflets that turn yellow in the fall As its common name implies, this tree produces a bitter tasting nut



Louisiana Plant Id Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory




Bitternut Hickory Natural Resource Stewardship
Bitternut hickory is a large, native north American tree, best reserved for larger landscapes It has large, compound leaves, a 1 inch, fourpart nut, and yellow fall color Like all hickories, debris from its fruit drops from late summer throughout autumn, makingBitternut Hickory (Carya cordiformis) The Bitternut Hickory, also called Swamp Hickory or Pignut Hickory, is a tall, slender tree growing 60 to 80 feet tall Its wood is used for lumber and pulpwood Wildlife such as deer and bear eat its mast Not edible for human consumption due to its bitter taste and high levels of tanninsOn average, Hickory is denser, stiffer, and harder than either White Oak or Hard Maple The wood is commonly used where strength or shockresistance is important Bitternut Hickory falls into the PecanHickory grouping, which tends to be slightly stabler but weaker than the TrueHickories, and is considered to be a semiringporous wood The strength characteristics of Pecan are




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




Hickory Tree Identification Gardenerdy
Identification There are 10 hickory species native to Tennessee bitternut, mockernut, pecan, pignut, red, sand, shagbark, shellbark, southern shagbark and water Two walnut species also are native — black walnut and butternut (or white walnut) Walnut trees are closely related to hickories, and they have many characteristics in common Bitternut Hickory The reddishbrown nuts of the bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) are bitter, but that doesn't stop squirrels and other animals from eating them Hardy in USDA zones 4 through 9, this tree has an oval crown and reaches a maximum height and spread of 80 and 50 feet, respectively Its bark is smooth and gray Did you know that pecan is a relative of the native bitternut hickory?
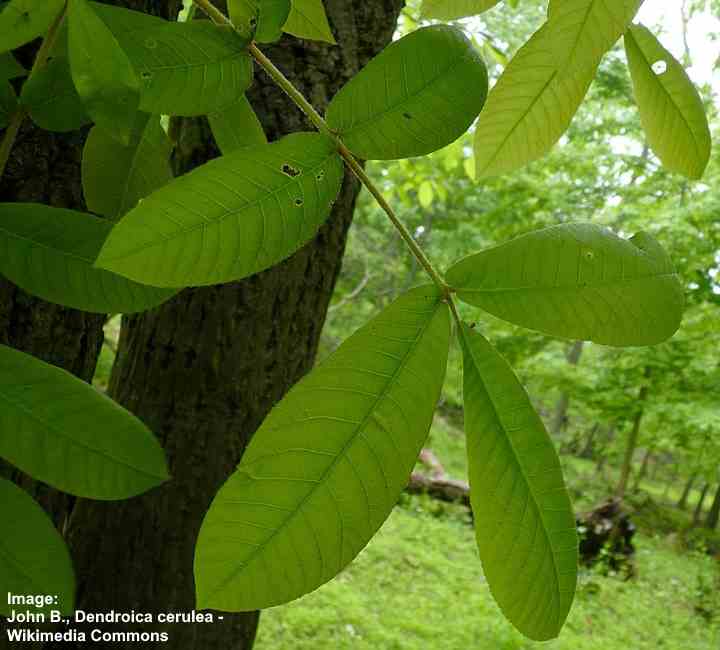




Hickory Trees Types Bark Leaves Nuts Pictures Identification




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis Wangenh K Koch
X y (z/4) = Total Points 368 Total Points Trunk Circumference 237 inches Height 106 feetAbout the Bitternut Hickory Tree Bitternut hickory trees, which are also commonly called swamp hickory trees, are very large deciduous trees that can live for up to 0 years in many cases They grow best when they're in moist soils, but they're tolerant of lots of soil types The wood produced by these wholesale hickory trees for saleThe buds are naked The buds are vibrant yellow I don't know of anything that is
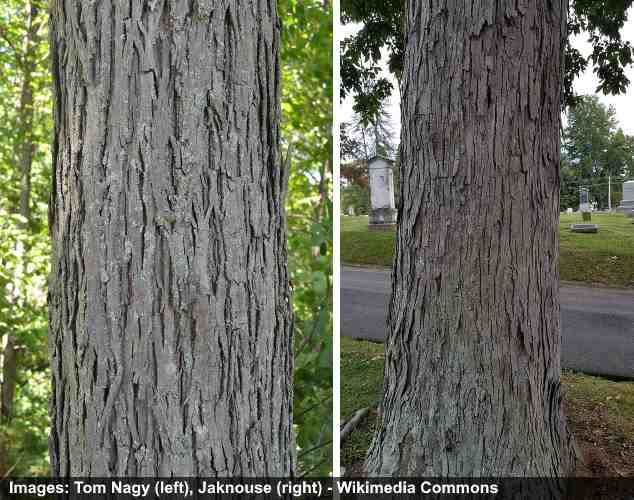




Hickory Trees Types Bark Leaves Nuts Pictures Identification




Bitternut Hickory Natural Resource Stewardship
Where to find Bitternut Hickory on the Louisiana State Arboretum Trails PAW Pawpaw Loop Trail 90 Refer to our Live Map to locate this species and its interpretative signage on the trail system Bitternut hickory is so easy to identify because the buds are extremely distinctive!Males are yellowgreen, drooping catkins with 3 hanging from one stalk, 3 to 4



Hickory How To Identify A Shagbark Hickory Tree In Indiana




Bitternut Hickory
Louisiana Plant ID Carya cordiformis (bitternut hickory) FAMILY JUGLANDACEAE ALTERNATE COMMON NAME LEAVES deciduous, alternate, oddpinnately compound, with 79 (11) sessile usually lanceolate leaflets, terminal leaflet about the same size as the upper laterals (maybe a little larger), lowermost lateral leaflets smallest, sometimes ovateThe species occurs on a wide range of sites, from dry upland sites in the southwestern part of its range to low wet woods in Louisiana (Fowells 1965, Grauke et al 1987) Bitternut is a major component of the White OakRed OakHickory forest in the northern US and of the Swamp Chestnut OakCherrybark Oak forest in the south (Fowells 1965)
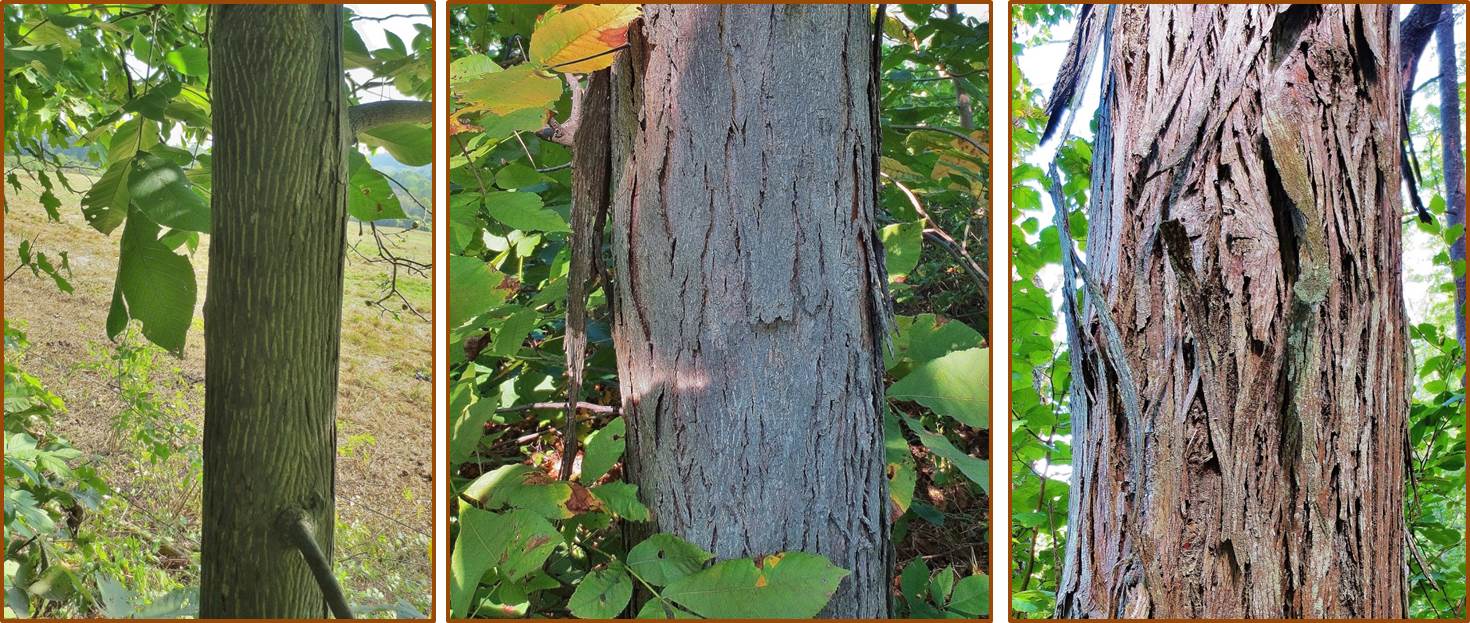




Hickory Nuts Foraging For Pignut And Shagbark Hickory Nuts




Identifying Hickory Trees Native To Tennessee Youtube



Bitternut Hickory Tree Icon Thin Linear Bitternut Hickory Tree Outline Icon Isolated On White Background From Nature Collection Stock Vector Illustration Of America Beautiful




File Bitternut Leaves And Fruits Jpg Wikimedia Commons
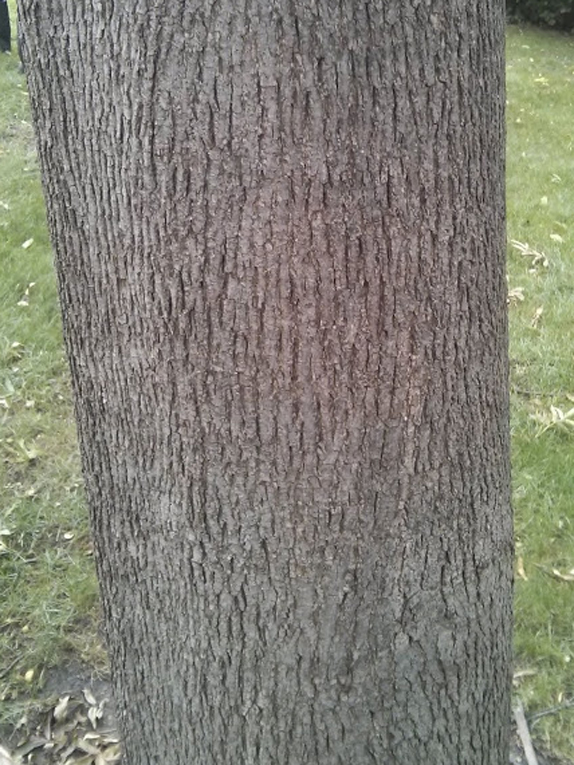




Basic Tree Tree Identification Regional And Community Forestry School Of Natural Resources Unviersity Of Nebraska Lincoln
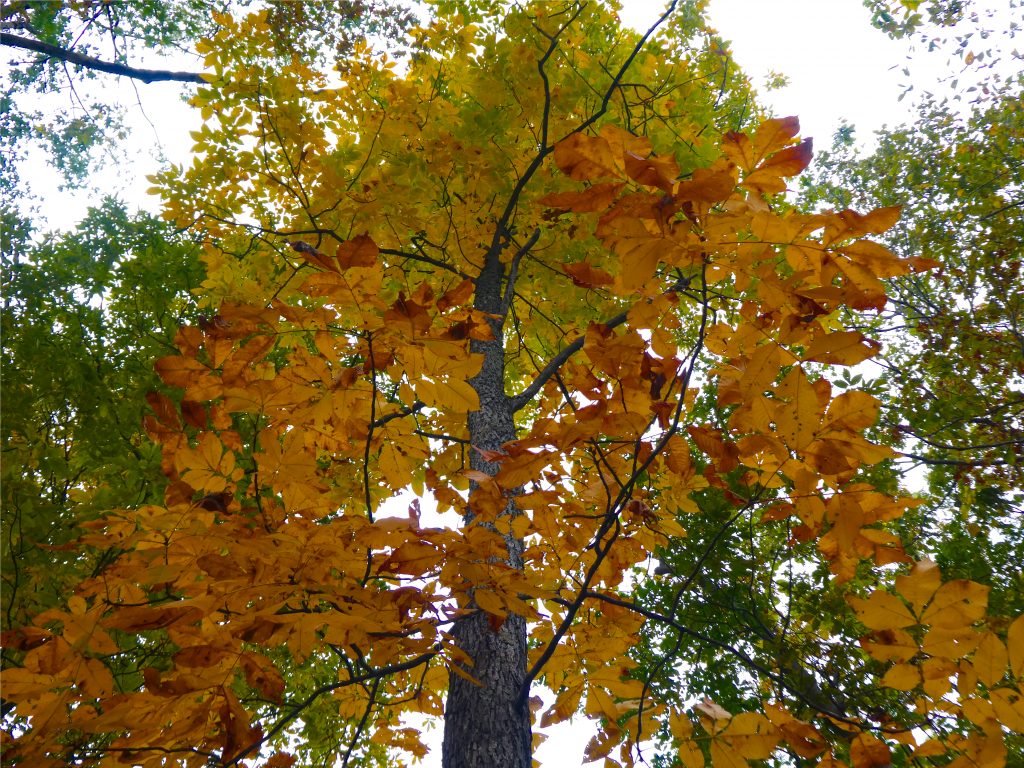




Hickory Trees What You Need To Know Our Guide




Hickory Tree Pictures




Plant Identification Closed Tree Identification Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis 1 By Kdjoergensen



Hickory Wood All Qd Up




12 Types Of Hickory Trees Leaves Bark And Nuts Identification Guide
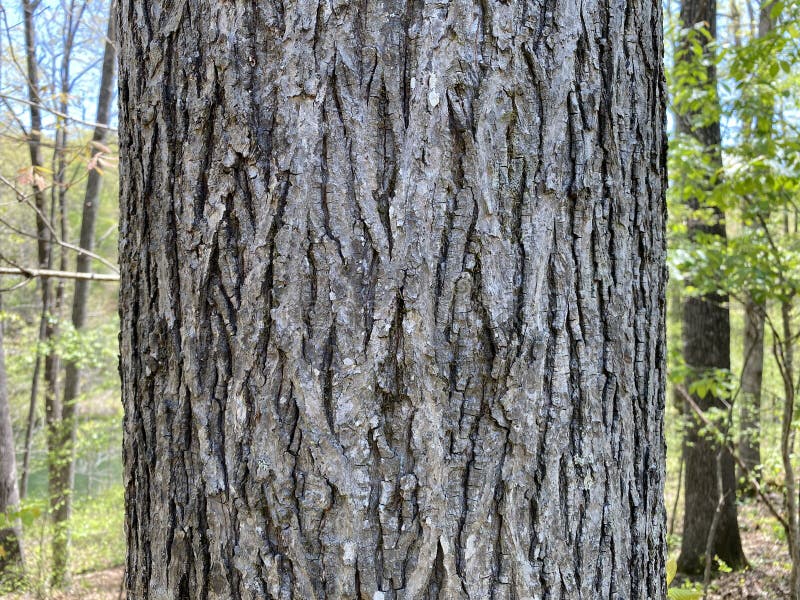




Tree Identification Tree Bark Pignut Hickory Carya Glabra Stock Image Image Of Furrows Pignut




Bitternut Hickory Missouri Department Of Conservation



1




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory Go Botany



Tree Species




Bitternut Hickory



Virginia Tech Dendrology Fact Sheet




How To Identify Hickory Trees 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




12 Types Of Hickory Trees Leaves Bark And Nuts Identification Guide




A Beginner S Guide How To Identify Hickory Nuts Mossy Oak



Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis
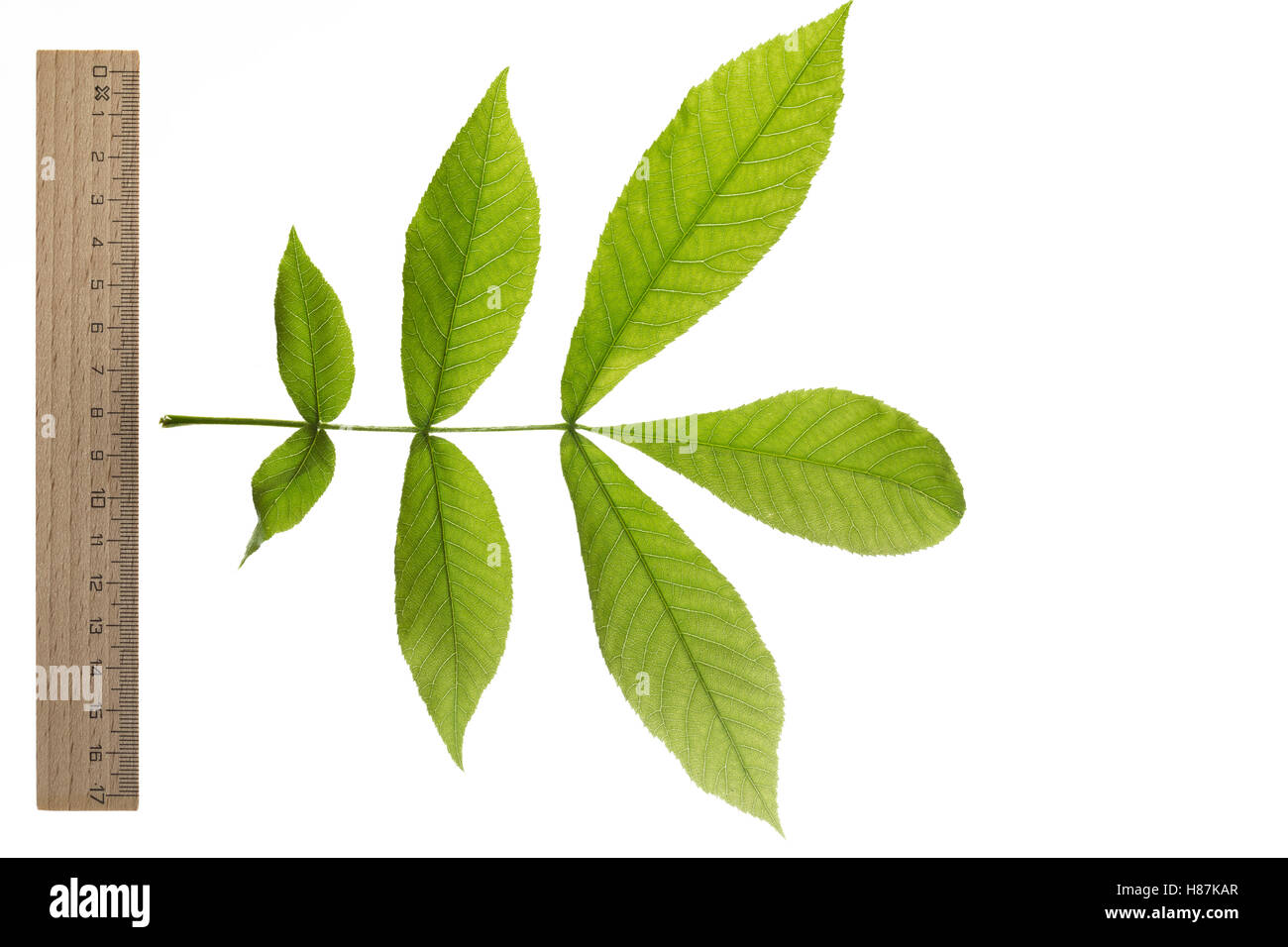




Bitternuss Bitternuss Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory Le Caryer Cordiforme Blatt Blatter Leaf Leaves Stock Photo Alamy




Flowers Bitternut Image Photo Free Trial Bigstock



Minnesota Seasons Bitternut Hickory




Bitternut Hickory Tree Of The Weeek Tree Identification Trees And Shrubs Hickory Tree
/hickory-ash-walnut-and-pecan-tree-leaf-key-1343477_FINAL-2fa028e259894c12a3094a2420f4c5eb.png)



Trees With Pinnate Leaves Hickory Ash Walnuts



Minnesota Seasons Bitternut Hickory




How To Identify Hickory Trees 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow



1
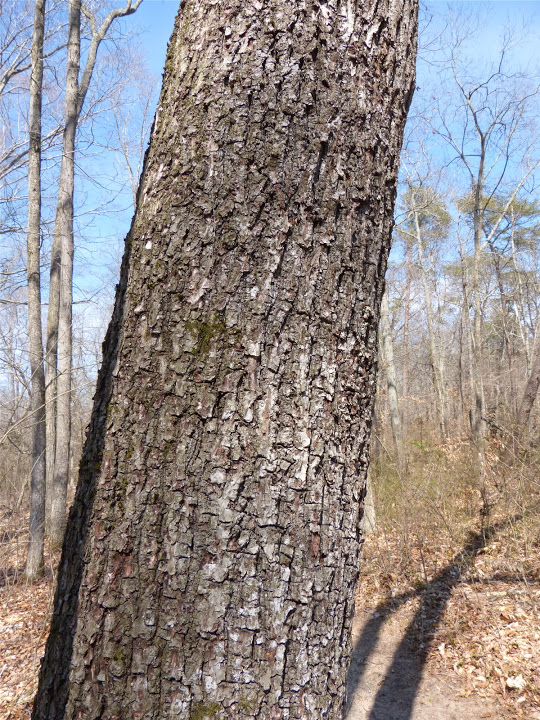




Maryland Biodiversity Project Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




University Of Illinois Extension Forestry We Are Doing A Deep Dive Into Tree Identification Using Twig Characteristics This Dormant Season Hickories Carya Spp Are A Group That Can Be Challenging To



Butternut Walnut Bitternut X
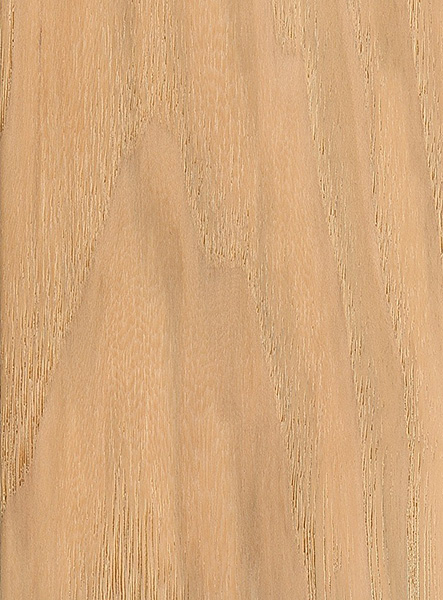




Bitternut Hickory The Wood Database Lumber Identification Hardwood



Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis



Bitternut Hickory
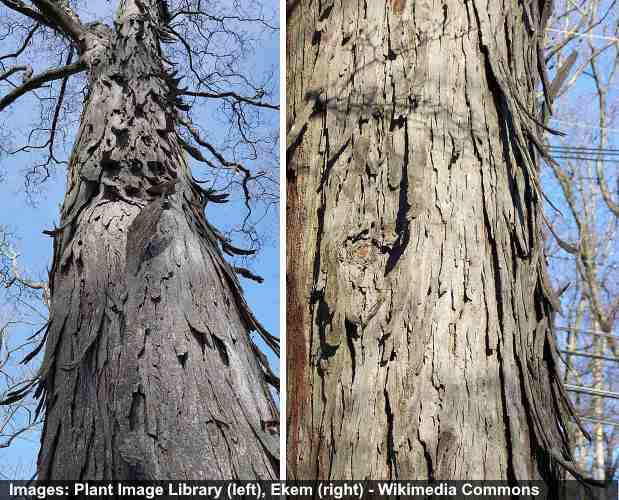




Hickory Trees Types Bark Leaves Nuts Pictures Identification
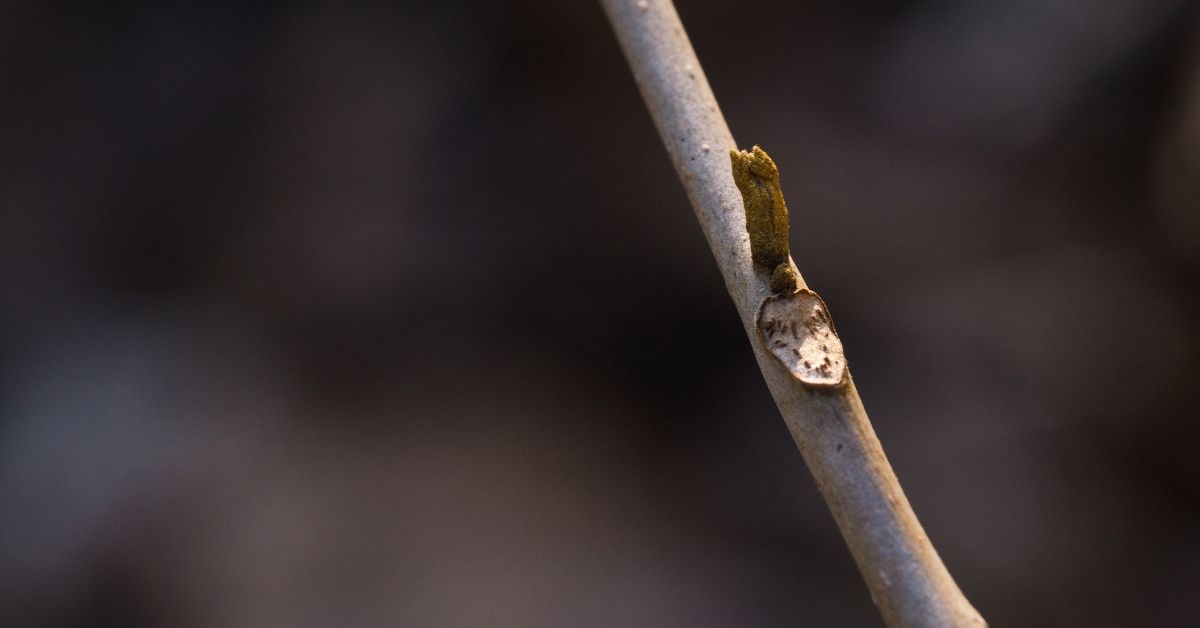




How To Identify Bitternut Hickory In The Winter Easy Feral Foraging



2
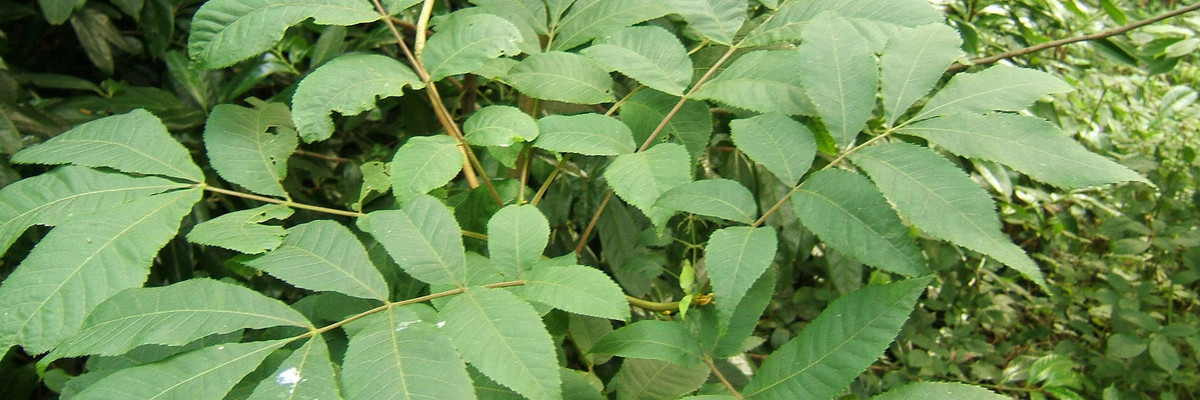




Bitternut Hickory Campus Trees




How To Identify Hickory Trees 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Trees With Don Leopold Bitternut Hickory Youtube



Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




Bitternut Hickory Bark Hickory Tree Tree Identification Tree Id




The Buckeye Botanist Care To Learn Your Carya S Hickories




Hickory Trees Lewisboro Field Guide
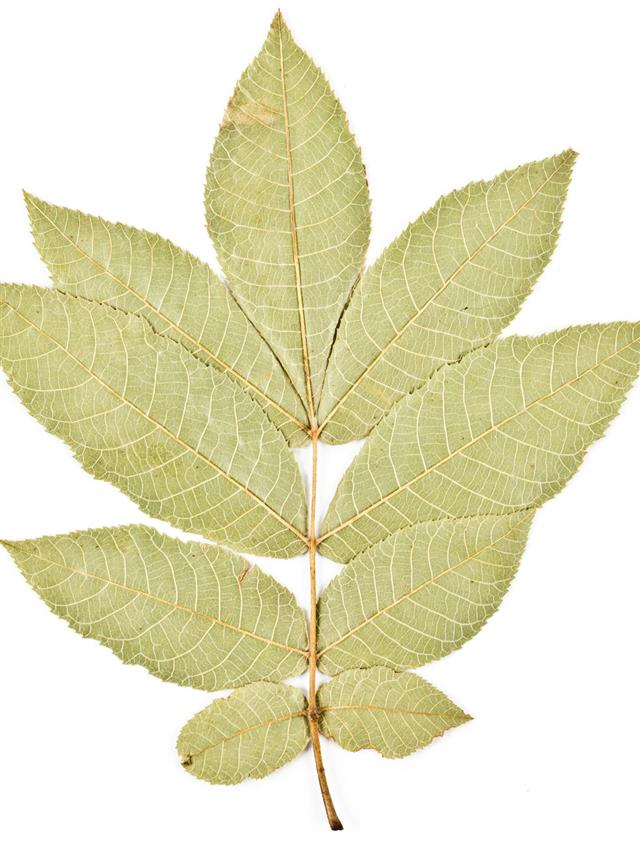




Hickory Tree Identification Gardenerdy




Virginia Tech Dendrology Fact Sheet




Bitternut Hickory Natural Resource Stewardship
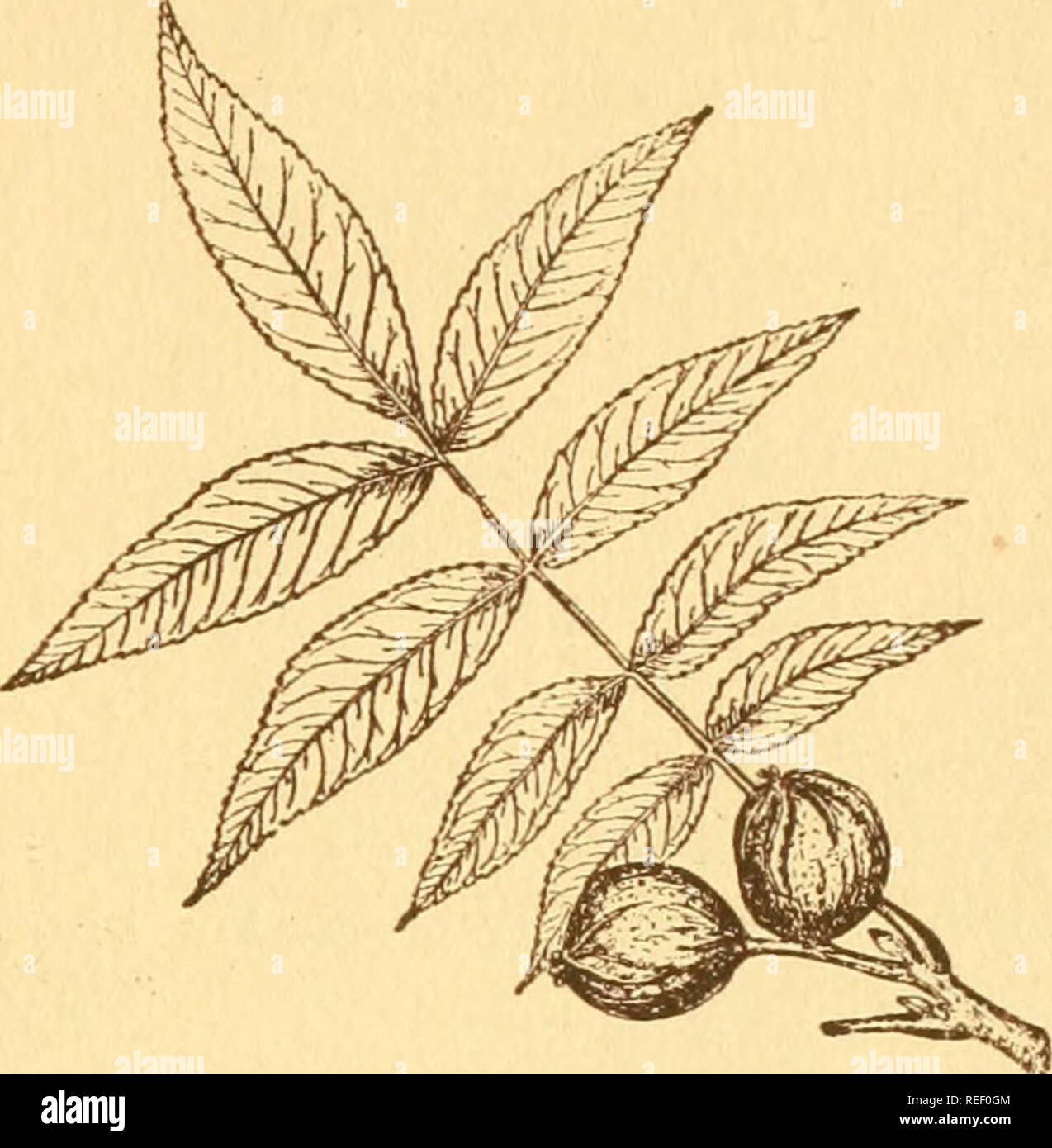



Common Trees Of New York Trees Trees Of New York 53 Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordifotmis Wangenheim X Koch The Bitternut Hickory Also Called Swamp Hickory And Water Hickory Is Usually Found



Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory Minnesota Wildflowers




Bitternut Hickory Ohio Department Of Natural Resources




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




Hickory Definition Tree Leaves Nut Facts Britannica




12 Types Of Hickory Trees Leaves Bark And Nuts Identification Guide




Carya Cordiformis Bitternut Hickory Go Botany




How To Identify Hickory Trees 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Recognizing Of Hickory Trees Youtube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1221455062-b189d4c031ef4cf2ac7b497f11ddd992.jpg)



The Major Hickory Species In North America




How To Identify Hickory Trees 13 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Hickories Of The Midwest Indigenous Landscapes
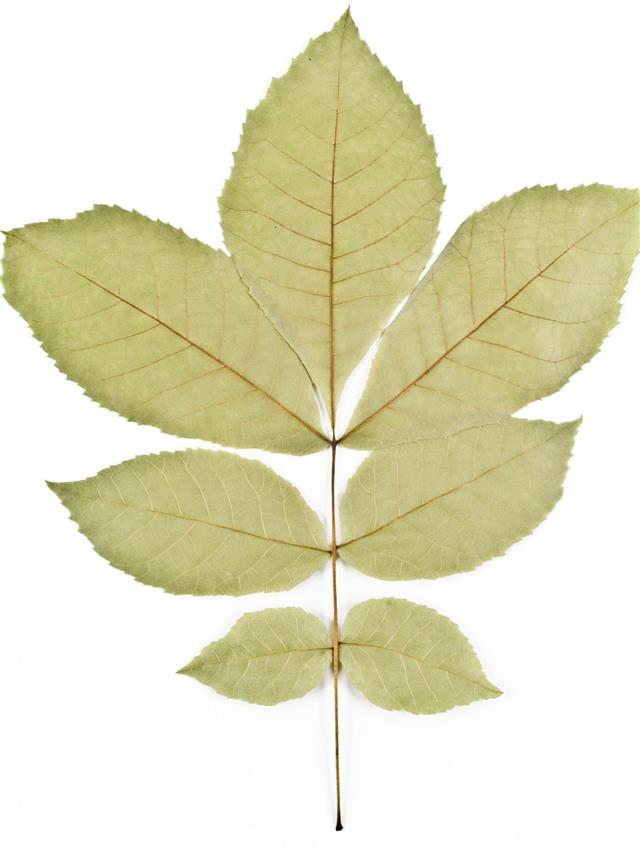




Hickory Tree Identification Gardenerdy




Bitternut Hickory Summer Leaf Clipart Free Download Transparent Png Creazilla




Hickory Trees Types Bark Leaves Nuts Pictures Identification




Bitternut Hickory Ohio Department Of Natural Resources




Bitternut Hickory Missouri Department Of Conservation




How To Forage And Harvest Hickory Nuts Survival Sullivan
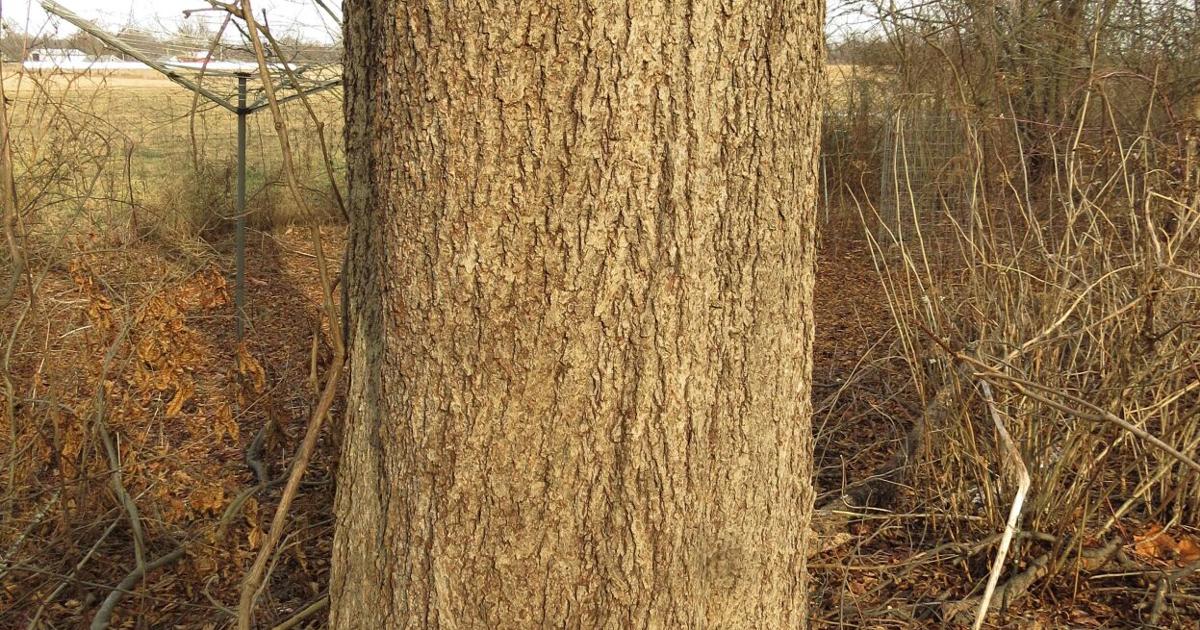




On Nature Column Bitternut Hickory Common To Indiana Woodlands Columns Heraldbulletin Com
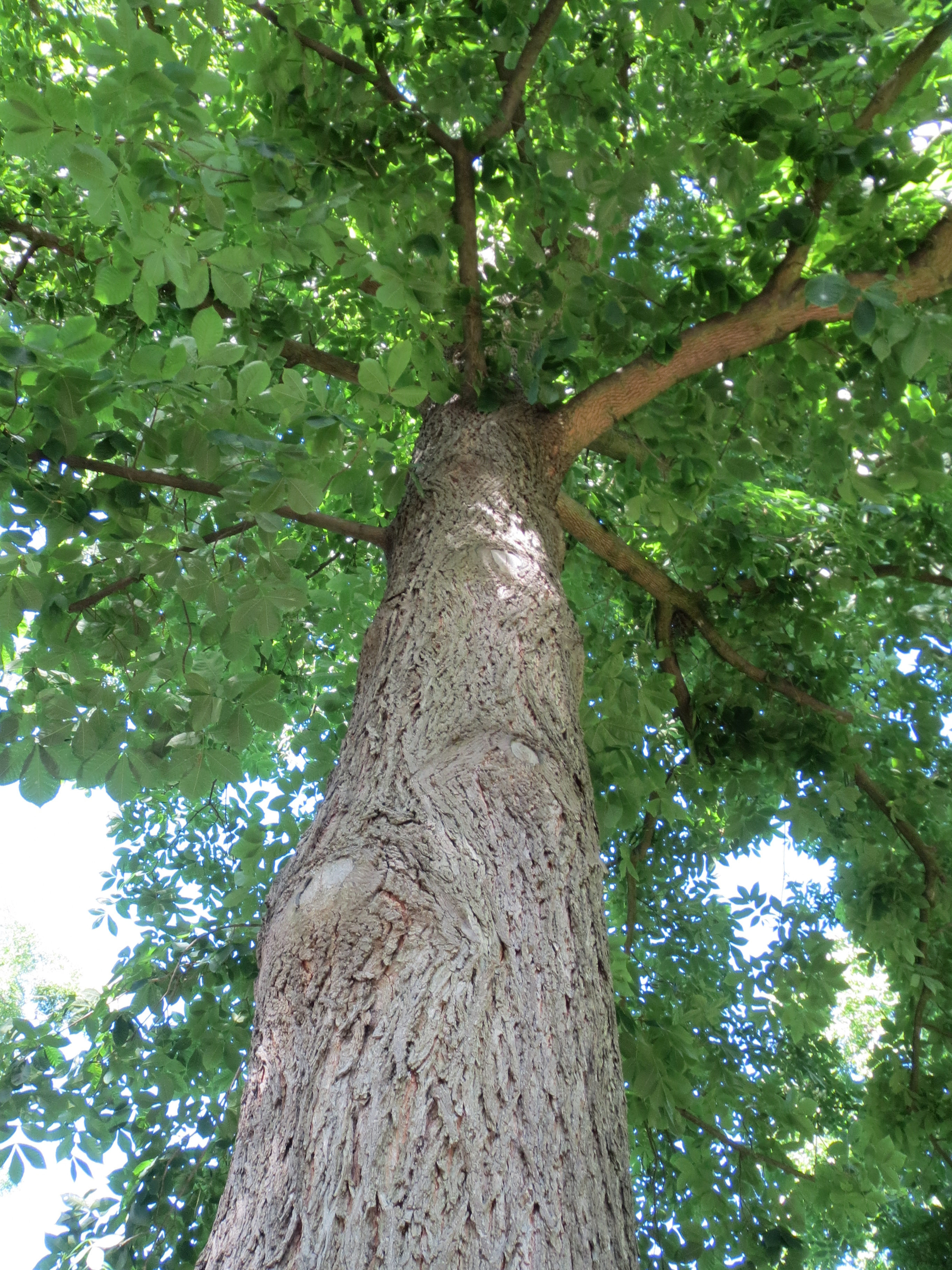




Bitternut Hickory Campus Trees
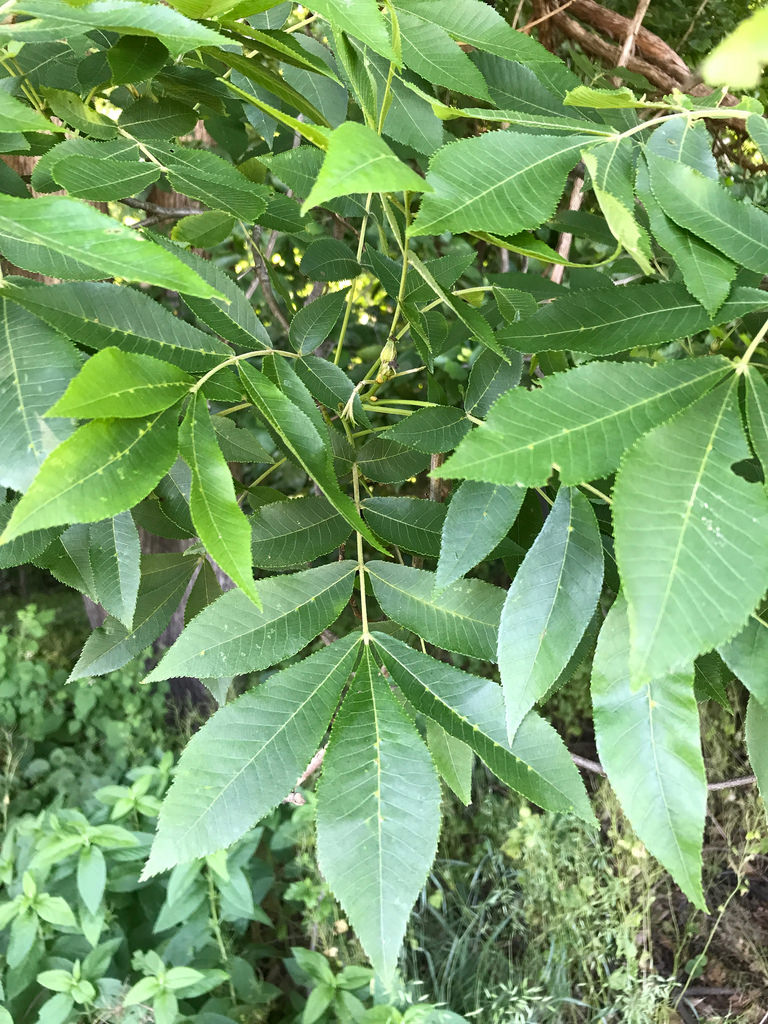




Maryland Biodiversity Project Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis
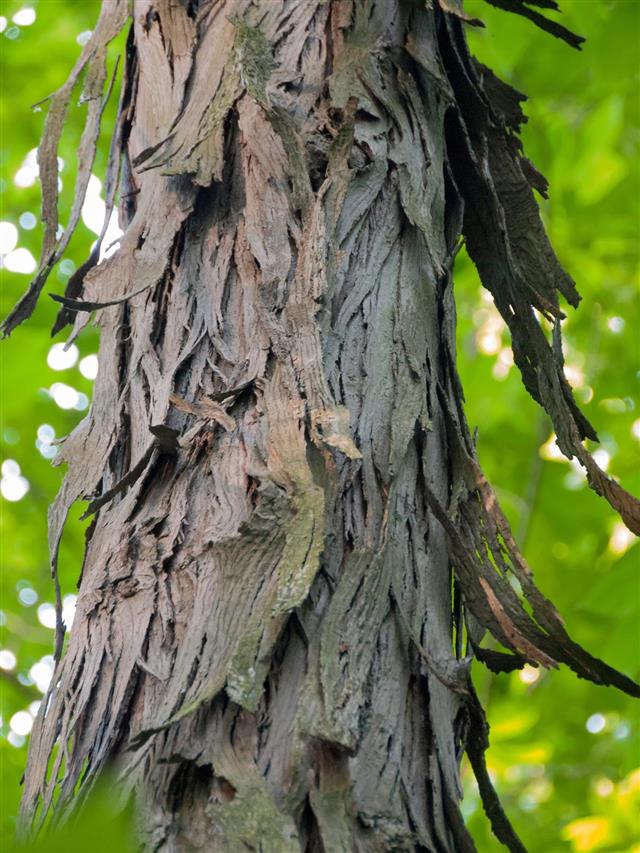




Hickory Tree Identification Gardenerdy
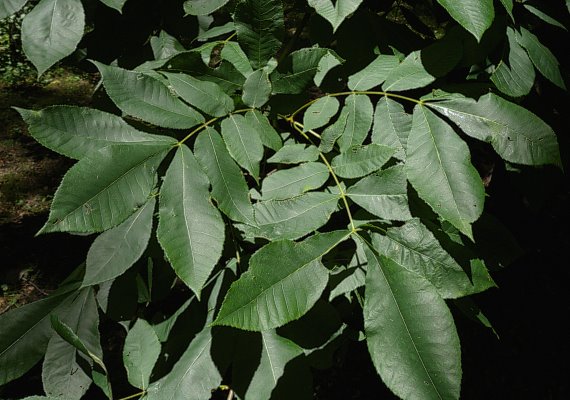




Bitternut Hickory Carya Cordiformis




The Buckeye Botanist Care To Learn Your Carya S Hickories
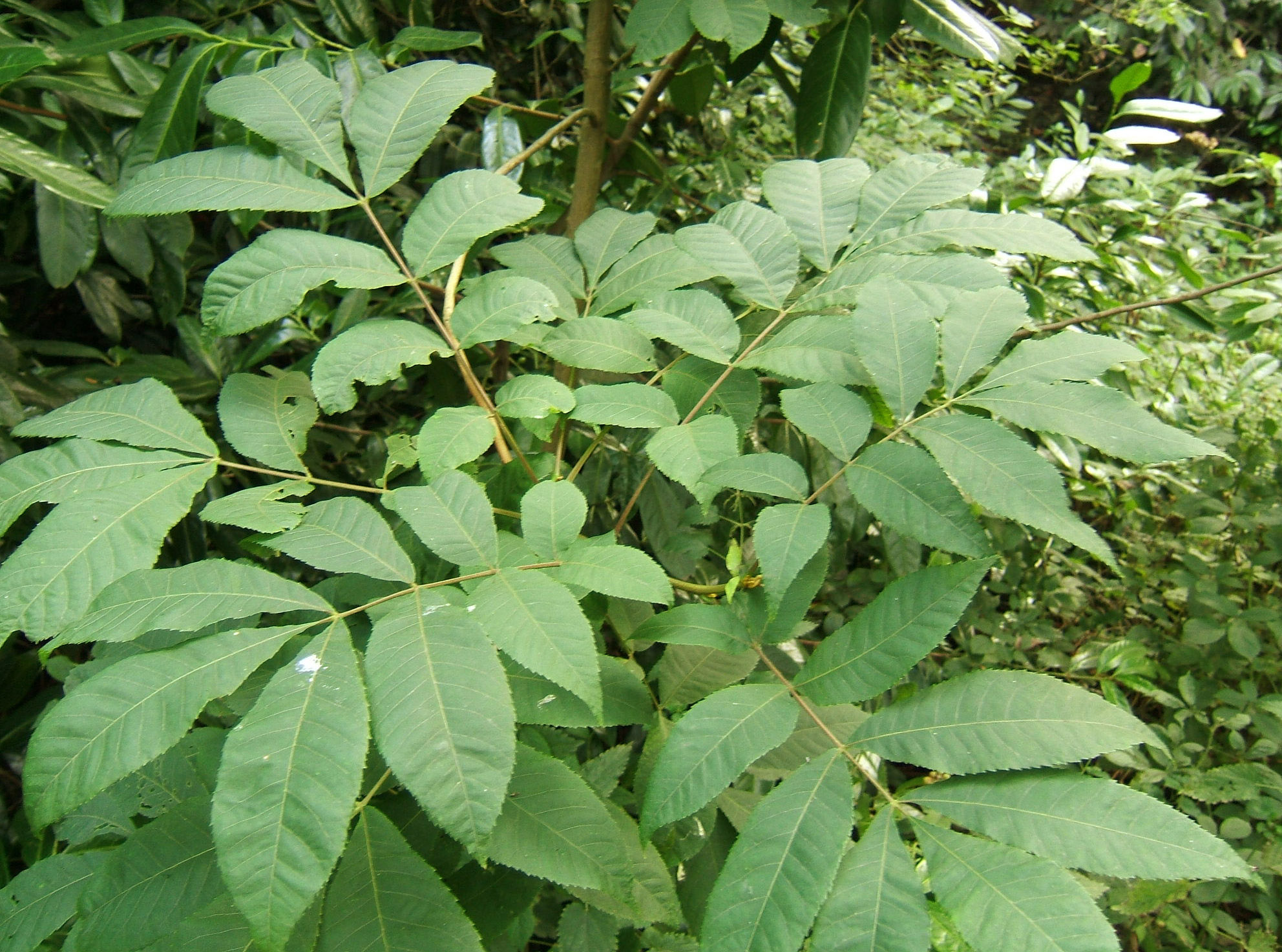




Carya Cordiformis Wikipedia



1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿